---
title: Connect from Prisma to Neon
subtitle: Learn how to connect to Neon from Prisma
enableTableOfContents: true
redirectFrom:
- /docs/quickstart/prisma
- /docs/integrations/prisma
- /docs/guides/prisma-guide
- /docs/guides/prisma-migrate
updatedOn: '2025-10-24T12:53:27.789Z'
---
Prisma is an open-source, next-generation ORM that lets you to manage and interact with your database. This guide covers the following topics:
- [Connect to Neon from Prisma](#connect-to-neon-from-prisma)
- [Use connection pooling with Prisma](#use-connection-pooling-with-prisma)
- [Use the Neon serverless driver with Prisma](#use-the-neon-serverless-driver-with-prisma)
- [Connection timeouts](#connection-timeouts)
- [Connection pool timeouts](#connection-pool-timeouts)
- [JSON protocol for large Prisma schemas](#json-protocol-for-large-prisma-schemas)
## Connect to Neon from Prisma
To establish a basic connection from Prisma to Neon, perform the following steps:
1. Retrieve your Neon connection string. You can find it by clicking the **Connect** button on your **Project Dashboard**. Select a branch, a user, and the database you want to connect to. A connection string is constructed for you.
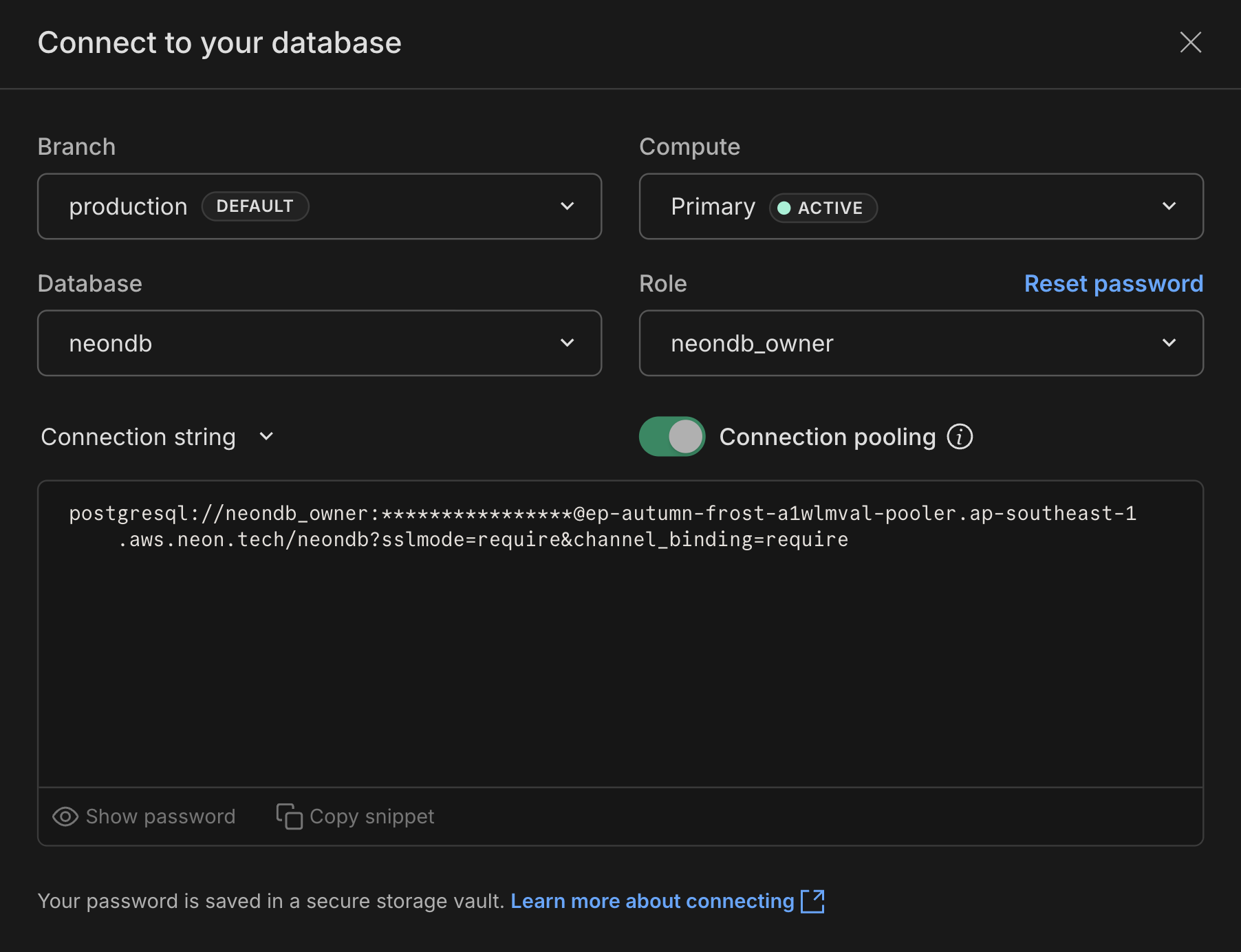
The connection string includes the user name, password, hostname, and database name.
2. Add the following lines to your `prisma/schema.prisma` file to identify the data source and database URL:
```typescript
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
```
3. Add a `DATABASE_URL` variable to your `.env` file and set it to the Neon connection string that you copied in the previous step. We also recommend adding `?sslmode=require&channel_binding=require` to the end of the connection string to ensure a [secure connection](/docs/connect/connect-securely).
Your setting will appear similar to the following:
```text shouldWrap
DATABASE_URL="postgresql://[user]:[password]@[neon_hostname]/[dbname]?sslmode=require&channel_binding=require"
```
If you plan to use Prisma Client from a serverless function, see [Use connection pooling with Prisma](#use-connection-pooling-with-prisma) for additional configuration instructions. To adjust your connection string to avoid connection timeout issues, see [Connection timeouts](#connection-timeouts).
## Use connection pooling with Prisma
Serverless functions can require a large number of database connections as demand increases. If you use serverless functions in your application, we recommend that you use a pooled Neon connection string, as shown:
```ini shouldWrap
# Pooled Neon connection string
DATABASE_URL="postgresql://alex:AbC123dEf@ep-cool-darkness-123456-pooler.us-east-2.aws.neon.tech/dbname?sslmode=require&channel_binding=require"
```
A pooled Neon connection string adds `-pooler` to the endpoint ID, which tells Neon to use a pooled connection. You can add `-pooler` to your connection string manually or copy a pooled connection string from **Connect to your database** modal — click **Connect** on your Project Dashboard to open the modal.
### Connection pooling with Prisma Migrate
Prior to Prisma ORM 5.10, attempting to run Prisma Migrate commands, such as `prisma migrate dev`, with a pooled connection caused the following error:
```text
Error undefined: Database error
Error querying the database: db error: ERROR: prepared statement
"s0" already exists
```
To avoid this issue, you can define a direct connection to the database for Prisma Migrate or you can upgrade Prisma ORM to 5.10 or higher.
#### Using a direct connection to the database
You can configure a direct connection while allowing applications to use Prisma Client with a pooled connection by adding a `directUrl` property to the datasource block in your `schema.prisma` file. For example:
```typescript
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
directUrl = env("DIRECT_URL")
}
```
The `directUrl` property is available in Prisma version [4.10.0](https://github.com/prisma/prisma/releases/tag/4.10.0) and higher. For more information about this property, refer to the [Prisma schema reference](https://www.prisma.io/docs/reference/api-reference/prisma-schema-reference#fields).
After adding the `directUrl` property to your `schema.prisma` file, update the `DATABASE_URL` and `DIRECT_URL` variables settings in your `.env` file:
1. Set `DATABASE_URL` to the pooled connection string for your Neon database. Applications that require a pooled connection should use this connection.
1. Set `DIRECT_URL` to the direct (non-pooled) connection string. This is the direct connection to the database required by Prisma Migrate. Other Prisma CLI operations may also require a direct connection.
When you finish updating your `.env` file, your variable settings should appear similar to the following:
```ini shouldWrap
# Pooled Neon connection string
DATABASE_URL="postgresql://alex:AbC123dEf@ep-cool-darkness-123456-pooler.us-east-2.aws.neon.tech/dbname?sslmode=require&channel_binding=require"
# Unpooled Neon connection string
DIRECT_URL="postgresql://alex:AbC123dEf@ep-cool-darkness-123456.us-east-2.aws.neon.tech/dbname?sslmode=require&channel_binding=require"
```
#### Using a pooled connection with Prisma Migrate
With Prisma ORM 5.10 or higher, you can use a pooled Neon connection string with Prisma Migrate. In this case, you only need to define the pooled connection string in your `schema.prisma` file. Adding a `directUrl` property to the datasource block in your `schema.prisma` file and defining a `DIRECT_URL` setting in your environment file are not required. Your complete configuration will look like this:
`schema.prisma` file:
```typescript
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
```
`.env` file:
```ini
# Pooled Neon connection string
DATABASE_URL="postgresql://alex:AbC123dEf@ep-cool-darkness-123456-pooler.us-east-2.aws.neon.tech/dbname?sslmode=require&channel_binding=require"
```
## Use the Neon serverless driver with Prisma
The Neon serverless driver is a low-latency Postgres driver for JavaScript and TypeScript that lets you query data from serverless and edge environments. For more information about the driver, see [Neon serverless driver](/docs/serverless/serverless-driver).
To set up Prisma with the Neon serverless driver, use the Prisma driver adapter. This adapter allows you to choose a different database driver than Prisma's default driver for communicating with your database.
The Prisma driver adapter feature is available in **Preview** in Prisma version 5.4.2 and later.
To get started, enable the `driverAdapters` Preview feature flag in your `schema.prisma` file, as shown:
```javascript
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client-js"
previewFeatures = ["driverAdapters"]
}
datasource db {
provider = "postgresql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
```
Next, generate the Prisma Client:
```bash
npx prisma generate
```
Install the Prisma adapter for Neon, the Neon serverless driver, and `ws` packages:
```bash
npm install ws @prisma/adapter-neon @neondatabase/serverless
npm install -D @types/ws
```
Update your Prisma Client instance:
```javascript
import 'dotenv/config';
import { PrismaClient } from '@prisma/client';
import { PrismaNeon } from '@prisma/adapter-neon';
import { neonConfig } from '@neondatabase/serverless';
import ws from 'ws';
neonConfig.webSocketConstructor = ws;
// To work in edge environments (Cloudflare Workers, Vercel Edge, etc.), enable querying over fetch
// neonConfig.poolQueryViaFetch = true
// Type definitions
// declare global {
// var prisma: PrismaClient | undefined
// }
const connectionString = `${process.env.DATABASE_URL}`;
const adapter = new PrismaNeon({ connectionString });
const prisma = global.prisma || new PrismaClient({ adapter });
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') global.prisma = prisma;
export default prisma;
```
You can now use Prisma Client as you normally would with full type-safety. Prisma Migrate, introspection, and Prisma Studio will continue working as before, using the Neon connection string defined by the `DATABASE_URL` variable in your `schema.prisma` file.
If you encounter a `TypeError: bufferUtil.mask is not a function` error when building your application, this is likely due to a missing dependency that the `ws` module requires when using `Client` and `Pool` constructs. You can address this requirement by installing the `bufferutil` package:
```shell
npm i -D bufferutil
```
## Connection timeouts
A connection timeout that occurs when connecting from Prisma to Neon causes an error similar to the following:
```text shouldWrap
Error: P1001: Can't reach database server at `ep-white-thunder-826300.us-east-2.aws.neon.tech`:`5432`
Please make sure your database server is running at `ep-white-thunder-826300.us-east-2.aws.neon.tech`:`5432`.
```
This error most likely means that the Prisma query engine timed out before the Neon compute was activated.
A Neon compute has two main states: _Active_ and _Idle_. Active means that the compute is currently running. If there is no query activity for 5 minutes, Neon places a compute into an idle state by default.
When you connect to an idle compute from Prisma, Neon automatically activates it. Activation typically happens within a few seconds but added latency can result in a connection timeout. To address this issue, you can adjust your Neon connection string by adding a `connect_timeout` parameter. This parameter defines the maximum number of seconds to wait for a new connection to be opened. The default value is 5 seconds. A higher setting may provide the time required to avoid connection timeouts. For example:
```text shouldWrap
DATABASE_URL="postgresql://[user]:[password]@[neon_hostname]/[dbname]?sslmode=require&channel_binding=require&connect_timeout=10"
```
A `connect_timeout` setting of 0 means no timeout.
## Connection pool timeouts
Another possible cause of timeouts is [Prisma's connection pool](https://www.prisma.io/docs/concepts/components/prisma-client/working-with-prismaclient/). The Prisma query engine manages a pool of connections. The pool is instantiated when a Prisma Client opens a first connection to the database. For an explanation of how this connection pool functions, read [How the connection pool works](https://www.prisma.io/docs/concepts/components/prisma-client/working-with-prismaclient/connection-pool#how-the-connection-pool-works), in the _Prisma documentation_.
The default size of the Prisma connection pool is determined by the following formula: `num_physical_cpus * 2 + 1`, where `num_physical_cpus` represents the number of physical CPUs on the machine where your application runs. For example, if your machine has four physical CPUs, your connection pool will contain nine connections (4 \* 2 + 1 = 9). As mentioned in the [Prisma documentation](https://www.prisma.io/docs/concepts/components/prisma-client/working-with-prismaclient/connection-pool#default-connection-pool-size), this formula is a good starting point, but the recommended connection limit also depends on your deployment paradigm — particularly if you are using serverless. You can specify the number of connections explicitly by setting the `connection_limit` parameter in your database connection URL. For example:
```text shouldWrap
DATABASE_URL="postgresql://[user]:[password]@[neon_hostname]/[dbname]?sslmode=require&channel_binding=require&connect_timeout=15&connection_limit=20"
```
For configuration guidance, refer to Prisma's [Recommended connection pool size guide](https://www.prisma.io/docs/guides/performance-and-optimization/connection-management#recommended-connection-pool-size).
In addition to pool size, you can configure a `pool_timeout` setting. This setting defines the amount of time the Prisma Client query engine has to process a query before it throws an exception and moves on to the next query in the queue. The default `pool_timeout` setting is 10 seconds. If you still experience timeouts after increasing `connection_limit` setting, you can try setting the `pool_timeout` parameter to a value larger than the default (10 seconds). For configuration guidance, refer to [Increasing the pool timeout](https://www.prisma.io/docs/guides/performance-and-optimization/connection-management#increasing-the-pool-timeout), in the _Prisma documentation_.
```text shouldWrap
DATABASE_URL="postgresql://[user]:[password]@[neon_hostname]/[dbname]?sslmode=require&channel_binding=require&connect_timeout=15&connection_limit=20&pool_timeout=15"
```
You can disable pool timeouts by setting `pool_timeout=0`.
## JSON protocol for large Prisma schemas
If you are working with a large Prisma schema, Prisma recently introduced a `jsonProtocol` wire protocol feature that expresses queries using `JSON` instead of GraphQL. The JSON implementation uses less CPU and memory, which can help reduce latencies when connecting from Prisma.
`jsonProtocol` is the default wire protocol as of Prisma version 5.0.0. If you run Prisma version 5.0.0 or later, you are already using the new protocol. If you run Prisma version 4 or earlier, you must use a feature flag to enable the `jsonProtocol`. You can read more about this feature here: [jsonProtocol changes](https://www.prisma.io/docs/guides/upgrade-guides/upgrading-versions/upgrading-to-prisma-5/jsonprotocol-changes).
## Learn more
For additional information about connecting from Prisma, refer to the following resources in the _Prisma documentation_:
- [Connection management](https://www.prisma.io/docs/guides/performance-and-optimization/connection-management)
- [Database connection issues](https://www.prisma.io/dataguide/managing-databases/database-troubleshooting#database-connection-issues)
- [PostgreSQL database connector](https://www.prisma.io/docs/concepts/database-connectors/postgresql)
- [Increasing the pool timeout](https://www.prisma.io/docs/guides/performance-and-optimization/connection-management#increasing-the-pool-timeout)
- [Schema migration with Neon Postgres and Prisma ORM](/docs/guides/prisma-migrations)